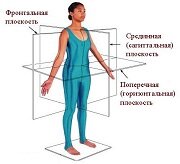
ПОЗНАВАТЕЛЬНОЕ Сила воли ведет к действию, а позитивные действия формируют позитивное отношение Как определить диапазон голоса - ваш вокал Игровые автоматы с быстрым выводом Как самому избавиться от обидчивости Противоречивые взгляды на качества, присущие мужчинам Вкуснейший "Салат из свеклы с чесноком" Натюрморт и его изобразительные возможности Применение, как принимать мумие? Мумие для волос, лица, при переломах, при кровотечении и т.д. Как научиться брать на себя ответственность Зачем нужны границы в отношениях с детьми? Световозвращающие элементы на детской одежде Как победить свой возраст? Восемь уникальных способов, которые помогут достичь долголетия Классификация ожирения по ИМТ (ВОЗ) Глава 3. Завет мужчины с женщиной Оси и плоскости тела человека - Тело человека состоит из определенных топографических частей и участков, в которых расположены органы, мышцы, сосуды, нервы и т.д.
| Задание 5 Определите является ли утверждение
Animals have not long held an important place in psychological laboratories as experimental subjects. а) ложным b) истинным с) в тексте нет информации
Прочитайте текст 3 и выполните задания. Types of Memory Memory (psychology), processes by which people and other organisms encode, store, and retrieveinformation. Encoding refers to the initial perception and registration of information. Storage is the retention of encoded information over time. Retrieval refers to the processes involved in using stored information. Whenever people successfully recall a prior experience, they must have encoded, stored, and retrieved information about the experience. Conversely, memory failure, for example, forgetting an important fact, reflects a breakdown in one of these stages of memory. Memory is critical to humans and all other living organisms. Practically, all of our daily activities: talking, understanding, reading, socializing depend on our having learned and stored information about our environments. Memory allows us to retrieve events from the distant past or from moments ago. It enables us to learn new skills and to form habits. Without the ability to access past experiences or information, we would be unable to comprehend language, recognize our friends and family members, find our way home, or even tie a shoe. Life would be a series of disconnected experiences, each one new and unfamiliar. Without any sort of memory, humans would quickly perish. Philosophers, psychologists, writers, and other thinkers have long been fascinated by memory. Among their questions: How does the brain store memory? Why do people remember some bits of information but not others? Can people improve their memories? What is the capacity of memory? Memory and learning are closely related, and the terms often describe roughly the same processes. The term learning is often used to refer to processes involved in the initial acquisition or encoding of information, whereas the term memory more often refers to later storage and retrieval of information. However, this distinction is not hard and fast. After all, information is learned only when it can be retrieved later, and retrieval cannot occur unless information was learned. Thus, psychologists often refer to the learning/memory process as a means of incorporating all facts of encoding, storage, and retrieval. Most theoretical models of memory distinguish three main systems: sensory memory, short-term or working memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory refers to the initial, momentary recording of information in our sensory systems. When sensations strike our eyes, they linger briefly in the visual system.. Psychologists originally used the term short-term memory to refer to the ability to hold information in mind over a brief period of time. We can keep information circulating in working memory by rehearsing it. Forgetting can occur rapidly from working memory. The term long-term memory is somewhat of a catch-all phrase because it can refer to facts learned a few minutes ago, personal memories many decades old, or skills learned with practice. Generally, however, long-term memory describes a system in the brain that can store vast amounts of information on a relatively enduring basis. Psychologists have different theories about how information enters long-term memory. The traditional view is that short-term memory and long-term memory are arranged in a parallel rather than sequential fashion. That is, information may be registered simultaneously in the two systems.
Задание 1 Заполните пропуски: ………….. allows us to retrieve events from the distant past or from moments ago. a) Thinking b) Memory c) Attention Задание 2 Заполните пропуски: Most theoretical models of memory …………… three main systems: sensory memory, short-term or working memory, and long-term memory. a) define b) understand c) distinguish Задание 3 Заполните пропуски: Long-term memory describes a system in the brain that can ……… vast amounts of information on a relatively enduring basis. a) store b) know c) forget |