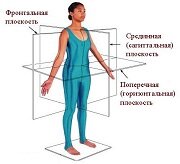
ПОЗНАВАТЕЛЬНОЕ Сила воли ведет к действию, а позитивные действия формируют позитивное отношение Как определить диапазон голоса - ваш вокал Игровые автоматы с быстрым выводом Как самому избавиться от обидчивости Противоречивые взгляды на качества, присущие мужчинам Вкуснейший "Салат из свеклы с чесноком" Натюрморт и его изобразительные возможности Применение, как принимать мумие? Мумие для волос, лица, при переломах, при кровотечении и т.д. Как научиться брать на себя ответственность Зачем нужны границы в отношениях с детьми? Световозвращающие элементы на детской одежде Как победить свой возраст? Восемь уникальных способов, которые помогут достичь долголетия Классификация ожирения по ИМТ (ВОЗ) Глава 3. Завет мужчины с женщиной Оси и плоскости тела человека - Тело человека состоит из определенных топографических частей и участков, в которых расположены органы, мышцы, сосуды, нервы и т.д.
| Доповніть речення дієсловами, даними в дужках у відповідному часі (the Simple Present Tense or Present Continuous Tense)
Example: Mr. Hansen often ___ (travel) to Atlanta on business. 1.Our class ___ (meet) three times every week. 2.Mr.Cole ___ (teach) us at present. He ___ (substitute) for Mr. Russell, who is our regular teacher. 3.At nine-thirty every morning our school bell ___ (ring). Listen! I believe it ___ (ring) now. 4.Stella ___ (watch) TV now. I believe that she always ___ (watch) a show at this time. 5.The wind always ___ (blow) hard in this section of town. 6.Klein ___ (have) a big sale on shoes today. 7.Kurt seems to be very busy. I guess he ___ (study) for his English test. 8.Ed usually ___ (stay) in the hotel when he ___ (come) to town, but tonight he ___ (stay) with us. 9.The sun always ___ (rise) in the east. Look! It ___ (rise) now. 10.Mr. and Mrs. Bush ___ (build) a new home on Hollywood Boulevard. Змініть форму даних речень із стверджувальної на запитальну і заперечну Example: You have worked very hard at your job. (You have not worked very hard at your job. Have you worked very hard at your job?) 1. I have spoken to Ms. Wolf about it. 2. They have returned home. 3. He has found his fountain pen. 4. He has told her all about it. 5. Mr. Garvin has left for San Francisco.
COURTS IN GREAT BRITAIN Civil courts deal with libel, disputes over the ownership of property, contested wills, divorces, etc. Civil cases are brought by a plaintiff against a defendant, and the lawyers who act for each side will hire barristers to plead their case in court. Often, cases involving damages /e.g. money to be paid as compensation to the victim of a road accident/ do not come to court. It is frequently more advantageous for the plaintiff to settle out of court for a slightly lower sum than he was asking and avoid the expenses and delay of a court action and even the possibility that the decision may go against him. In criminal cases, tried in the criminal courts, the plaintiff is the Crown, i.e. the Queen, as Head of State. Criminal cases pass through various stages. For minor offences the magistrates’ court is usually sufficient. This consists of three justices of the peace /J.P.’s/, who are respected of the local community, and presided over b a magistrate. If the accused so chooses he can be tried and sentenced by this court, which only as the power to impose limited sentences and fines. In more serious cases the defendant will be committed for trial in a higher court. Judges travel around the country, holding assizes in regional centres. At a major criminal trial, involving serious offences – armed robbery, grievous bodily harm, murder, etc. – the procedure will be more or less as follows. First, all the jurors are chosen – a jury consists of twelve people selected at random from the electoral roll – and both the prosecution and the defence have the right to challenge /to ask for the removal/ seven jurors. There are always enough people summoned for the jury service to make this possible. The counsel for the prosecution will address the jury and present his case, after which he will call witnesses /who swear to tell the truth, the whole truth and nothing but the truth/.The counsel for the defence has the right to cross-examine them. Then the counsel for the defence proceeds in the same way, though he may not call the defendant as the witness. Since the defendant is not obliged to give evidence. The judge nay intervene at any point and ask questions to clarify matters. After the two sides have presented their cases the judge gives his summing-up, which clarifies the points of law involved in the case. It is for the benefit of the jury as it’s their job to decide whether it has been proved that the defendant actually committed the crime with which he is charged. The jury retires to consider its verdict: Guilty or Not guilty. If the defendant is acquitted – all well and good, if he is convicted, then the judge will pass sentence on him. In this case the jury can recommend clemency in extenuating circumstances. Even if he sentences the defendant to prison, the judge can make it a suspended sentence, if the circumstances warrant it. Justice must only be done, it must be seen to be done. Find English equivalents in the text to the following words and phrases: 1)наклеп; 2)власність; 3)заповіт; 4)розлучення; 5)позивач та відповідач; 6)шкода (збитки); 7)головувати в суді; 8)накладати штраф; 9)віддати до суду; 10)виїздні засідання; 11)озброєне пограбування; 12)тяжке тілесне ушкодження; 13)вбивство; 14)обвинувачення; 15)захист; 16)перехресний допит; 17)свідчити; 18)скоїти злочин; 19)обвинувачувати у злочині; 20)виправдати; 21)пом’якшуючі обставини. |