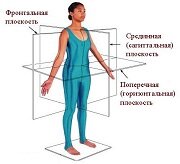
ПОЗНАВАТЕЛЬНОЕ Сила воли ведет к действию, а позитивные действия формируют позитивное отношение Как определить диапазон голоса - ваш вокал Игровые автоматы с быстрым выводом Как самому избавиться от обидчивости Противоречивые взгляды на качества, присущие мужчинам Вкуснейший "Салат из свеклы с чесноком" Натюрморт и его изобразительные возможности Применение, как принимать мумие? Мумие для волос, лица, при переломах, при кровотечении и т.д. Как научиться брать на себя ответственность Зачем нужны границы в отношениях с детьми? Световозвращающие элементы на детской одежде Как победить свой возраст? Восемь уникальных способов, которые помогут достичь долголетия Классификация ожирения по ИМТ (ВОЗ) Глава 3. Завет мужчины с женщиной Оси и плоскости тела человека - Тело человека состоит из определенных топографических частей и участков, в которых расположены органы, мышцы, сосуды, нервы и т.д.
| II. The notion of Rhetorical Image. Major Tropes. Lexical and Lexical-Syntactic Stylistic Devices.
STYLISTICS I. Phonetic Expressive means and Stylistic Devices The stylistic approach to the utterance is not confined to its structure and sense. There is another thing to be taken into account which in a certain type of communication plays an important role. This is the way a word, a phrase or a sentence sounds. The sound of most words taken separately will have little or no aesthetic value. It is in combination with other words that a word may acquire a desired phonetic effect. The way a separate word sounds may produce a certain euphonic effect, but this is a matter of individual perception and feeling and therefore subjective. The theory of sense - independence of separate sounds is based on a subjective interpretation of sound associations and has nothing to do with objective scientific data. However, the sound of a word, or more exactly the way words sound in combination, cannot fail to contribute something to the general effect of the message, particularly when the sound effect has been deliberately worked out. This can easily be recognized when analyzing alliterative word combinations or the rhymes in certain stanzas or from more elaborate analysis of sound arrangement. Phonetic repetitions: alliteration, rhyme, assonance Alliteration is a phonetic stylistic device which aims at imparting a melodic effect to the utterance. The essence of this device lies in the repetition of similar sounds, in particular consonant sounds, in close succession, particularly at the beginning of successive words: " The possessive instinct never stands still (J. Galsworthy) or, "Deep into the darkness peering, long I stood there wondering, fearing, doubting, dreaming dreams no mortals ever dared to dream before" (E. A. Poe). Alliteration, like most phonetic expressive means, does not bear any lexical or other meaning unless we agree that a sound meaning exists as such. But even so we may not be able to specify clearly the character of this meaning, and the term will merely suggest that a certain amount of information is contained in the repetition of sounds, as is the case with the repetition of lexical units.
Assonance – is the repetition of similar vowels, usually in stressed syllables. They both may produce the effect of euphony (a sense of ease and comfort in pronouncing or hearing) or cacophony (a sense of strain and discomfort in pronouncing or hearing). As an example of the first may serve the famous lines of E.A. Poe: ...silken sad uncertain rustling of each purple curtain... Rhyme is the repetition of identical or similar terminal sound combination of words. Rhyming words are generally placed at a regular distance from each other. In verse they are usually placed at the end of the corresponding lines. We distinguish between full rhymes(presupposes identity of the vowel sound and the following consonant sounds in a stressed syllable, including the initial consonant of the second syllable (in polysyllabic words), we have exact or identical rhymes) and incomplete rhymes(they can be divided into two main groups: vowel rhymes(the vowels of the syllables in corresponding words are identical) and consonant rhymes (show concordance in consonants and disparity in vowels, as in worth - forth, tale - tool -treble - trouble; flung – long). Compound or broken (modifications in rhyming sometimes go so far as to make one word rhyme with a combination of words; or two or even three words rhyme with a corresponding two or three words. The peculiarity of rhymes of this type is that the combination of words is made to sound like one word - a device which inevitably gives a colloquial and sometimes a humorous touch to the utterance). Sound imitating Onomatopoeia is a combination of speech sounds which alms at imitating sounds produced in nature (wind, sea, thunder, etc.) by things (machines or tools, etc.) by people (singing, laughter) and animals. Therefore the relation between onomatopoeia and the phenomenon it is supposed to represent is one of metonymy There are two varieties of onomatopoeia: direct and indirect. Direct onomatopoeiais contained in words that imitate natural sounds, as ding-dong, burr, bang, cuckoo. These words have different degrees of imitative quality. Some of them immediately bring to mind whatever it is that produces the sound. Others require the exercise of a certain amount of imagination to decipher it. Onomatopoetic words can be used in a transferred meaning, as for instance, ding - dong, which represents the sound of bells rung continuously, may mean 1) noisy, 2) strenuously contested. Indirect onomatopoeiademands some mention of what makes the sound, as rustling of curtains in the following line. And the silken, sad, uncertain rustling of each purple curtain. Indirect onomatopoeia is a combination of sounds the aim of which is to make the sound of the utterance an echo of its sense. It is sometimes called "echo writing". An example is: And the silken, sad, uncertain rustling of each purple curtain" (E. A. Poe), where the repetition of the sound [s] actually produces the sound of the rustling of the curtain.
II. The notion of Rhetorical Image. Major Tropes. Lexical and Lexical-Syntactic Stylistic Devices. Rhetorical image In philosophy "image" denotes the result of reflection of the object of reality in man's consciousness. On the sensible level our senses, ideas might be regarded as images. On a higher level of thinking images take the form of concepts, judgements, conclusions. Depending on the level of reflecting the objective reality ( sensual and conceptual) there are 2 types of images: 1. Art - reflects the objective reality inhuman life. While informing us of a phenomenon of life it simultaneously expresses our attitude towards it. 2. Literature - deals with a specific type of artistic images, verbal - is a pen - picture of a thing, person or idea expressed in a figurative way in their contextual meaning in music - sounds. The overwhelming majority of Iinguists agree that a word is the smallest unit being able to create images because it conveys the artistic reality and image. On this level the creation of images is the result of the interaction of two meanings: direct (denotation) and indirect (figurative). Lexical expressive meanings in which a word or word combination is used figuratively are called tropes. The verbal meaning has the following structure: 1. Tenor (direct thought) subjective; 2. Vehicle (figurative thought) objective; 3. Ground is the common feature of T and V; 4. The relation between T and V; 5. The technique of identification (The type of trope); |