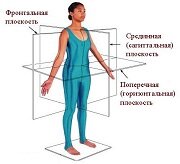
ПОЗНАВАТЕЛЬНОЕ Сила воли ведет к действию, а позитивные действия формируют позитивное отношение Как определить диапазон голоса - ваш вокал Игровые автоматы с быстрым выводом Как самому избавиться от обидчивости Противоречивые взгляды на качества, присущие мужчинам Вкуснейший "Салат из свеклы с чесноком" Натюрморт и его изобразительные возможности Применение, как принимать мумие? Мумие для волос, лица, при переломах, при кровотечении и т.д. Как научиться брать на себя ответственность Зачем нужны границы в отношениях с детьми? Световозвращающие элементы на детской одежде Как победить свой возраст? Восемь уникальных способов, которые помогут достичь долголетия Классификация ожирения по ИМТ (ВОЗ) Глава 3. Завет мужчины с женщиной Оси и плоскости тела человека - Тело человека состоит из определенных топографических частей и участков, в которых расположены органы, мышцы, сосуды, нервы и т.д.
| Higher Education in the USA
Устные темы и тексты к устным темам Тема №1 "Высшее образование в России" Text 1 HIGHER EDUCATION IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION Higher education in the Russian Federation There are four types of institutions of higher education in Russia at the present time: 1. Universities: responsible for education and research in a variety of disciplines; 2. Academies: responsible for education and research. They differ from universities only in that they restrict themselves to a single discipline; 3. Institutes: multi-discipline oriented. They can be independent structural units, or part of a university or academy; 4. Private institutions: present in increasing numbers. They offer degrees in non-engineering fields such as business, culture, sociology and religion, etc. Currently, there is a new degree structure which follows a three-level pattern and uses U.S./British nomenclature. The Certificate of Secondary Complete General Education and the successful passing of university matriculation exams are required for admission to all levels. Level Igenerally lasts 2 years of study, upon completion of which students are awarded a “certificate of incomplete higher education”. Students holding a Level I qualification may either continue their studies or, if they choose not to, leave the institution with the intermediate diploma. Level IIrepresents the completion of “basic academic education”. Students are awarded a Bachelor’s degree upon a completion of four-year programmes in the humanities, economics and natural sciences, as well as some practical professional training. Level IIIrepresents an educational level, common to both the Master’s degree and the Specialist diploma. Specialist:This is a professional training programme designed for the students who choose to pursue the practical applications of their specialization. It can be earned in one of two ways: a) upon completion of at least one year of study after the Bachelor’s degree; b) upon completion of five years of study after the certificate of secondary complete general education. The degree grants professional qualification in engineering, teaching, economics and etc. Master’s:This is an academic degree designed for students who wish to pursue a career in academy and research. The length of study is at least two years. The top level of higher education is a graduate work which entails a three-year programme of study and research leading to a Candidate degree, then original research which finally leads to a Doctoral degree. With more than 880 higher education institutions, the Russian Federation higher education system offers a broad range of study and research programmes designed to meet possible academic need on the part of students and these include: - intermediate diploma courses; - full Bachelor’s degree programmes (BA or BSc); - full Master’s degree programmes (MA or MSc); - Master’s degree programmes for graduates already holding a Bachelor’s degree; - special full-time courses for visiting students who commenced and/or will complete their degree at a foreign higher education institution; - doctoral programmes (PhD and DSc); - continuing education and training programmes; - research study programmes; - retraining programmes; - Specialist’s diploma programmes. Questions: 1. What are the main types of higher educational establishments in Russia? 2. How many levels are there in the system of higher education in Russia? What are they responsible for? 3. What are the main requirements for the admission to the educational establishments of all levels? 4. In which case are students awarded a “certificate of incomplete higher education” or a Bachelor’s degree? 5. What does level III represent? 6. How can the Specialist diploma be earned? 7. What is the difference between Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees? 8. What are the highest degree titles in Russia? 9. What are the most common study and research programmes offered in the institutions of higher education in Russia? Vocabulary 1. independent structural unit – независимые структурные подразделения 2. a three-level pattern - трехуровневая модель 3. a certificate of Secondary Complete General Education - аттестат о полном общем среднем образовании 4. to award a degree - присуждать степень 5. institution of higher education - высшее учебное заведение 6. to pass university matriculation exams - сдать вступительные экзамены в университет 7. professional training program - программа профессиональной подготовки 8. to wish to pursue a career in - желать продолжить карьеру в . . . . . области 9. to entail a tree-year program of study and research - предусмотреть трехгодичную программу обучения и исследовательской работы 10. retraining programs - программа переподготовки Text 2 Higher Education in the USA There are about 3,000 colleges and universities, both private and public, in the United States. They are all independent, offering their own choice of studies, setting their own admission standards and deciding which students meet those standards. The greater the prestige of the university, the higher the grades required. The terms "college" and "university" are often used interchangeably, as "college" is used to refer to all undergraduate education and the four-year undergraduate programme, leading to a bachelor's degree, can be followed at either college or university. Universities are larger than colleges and also have graduate schools where students can receive post-graduate education. During the first two years students usually follow general courses in the arts or sciences and then choose a major (the subject or area of studies in which they concentrate — the other subjects are called minors). Credits (with grades) are awarded for the successful completion of each course. These credits are often transferable, so students who have not done well in high school can choose a junior college (or community college), which offers a two-year "transfer" programme, preparing students for degree-granting institutions. Community colleges also offer two-year courses of a vocational nature, leading to technical and semi-professional occupations, such as journalism. Questions: 1. How many colleges and universities are there in the USA? 2. In what way are they independent? 3. What is the term college referred to? 4. How do universities differ from colleges? 5. What do students study during the first two years? 6. What are credits awarded for? 7. What does the term “transferable” mean? 8. What do community colleges offer? Vocabulary 1. admission standards - правила приема 2. interchangeable - равнозначный 3. undergraduate education - базовое университетское образование; four-year undergraduate program - четырехлетняя программа обучения для студентов 4. graduate school - аспирантура 5. a minor – неосновной, второстепенный предмет 6. to receive post-graduate education - получит послевузовское образование 7. to choose a major - выбирать специализацию 8. a junior college – неполный колледж; community college - районный колледж 9. transferable — переводной 10. to prepare students for degree-granting institution - готовить студентов для институтов, предоставляющих степень 11. to offer two-year courses of a vocational nature - предлагать двухлетние курсы, направленные на профессиональную подготовку Text 3 |