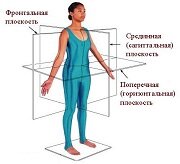
ПОЗНАВАТЕЛЬНОЕ Сила воли ведет к действию, а позитивные действия формируют позитивное отношение Как определить диапазон голоса - ваш вокал Игровые автоматы с быстрым выводом Как самому избавиться от обидчивости Противоречивые взгляды на качества, присущие мужчинам Вкуснейший "Салат из свеклы с чесноком" Натюрморт и его изобразительные возможности Применение, как принимать мумие? Мумие для волос, лица, при переломах, при кровотечении и т.д. Как научиться брать на себя ответственность Зачем нужны границы в отношениях с детьми? Световозвращающие элементы на детской одежде Как победить свой возраст? Восемь уникальных способов, которые помогут достичь долголетия Классификация ожирения по ИМТ (ВОЗ) Глава 3. Завет мужчины с женщиной Оси и плоскости тела человека - Тело человека состоит из определенных топографических частей и участков, в которых расположены органы, мышцы, сосуды, нервы и т.д.
| Teaching techniques of writing
LECTURE 10 TEACHING WRITING Competence in writing. Teaching techniques of writing. The aims of teaching writing at school. Types of writing and genres of communicating in writing. Stages of developing writing skills and activities used at them. Competence in writing and the aims of teaching writing at school Writing is a way of communicating with the help of graphic signs that let fix certain information to pass it through a distance and to keep it in space and time. Writing is not only a graphic system but it is also a communicative skill providing for expressing ideas in a graphic form.As any other kind of activity, writing is characterized by a motive (what for), the topic (the writer’s own ideas or rendering other people’s ideas), product (a written text of some type and genre) and result (changes in the addressee’s behavior). Since writing presupposes graphic form, not only the writer’s brain and speech organs are involved bur also hand motor analyzers. A specific feature of writing is the absence of direct contact with the communication partner. So the writer cannot correct their activity according to the partner’s reaction (it can only be predicted). It demands, in its turn, more coherence and cohesiveness, fewer contractions as everything should be maximally clear. On the other hand, the writer has more possibilities to work on both form and meaning of his utterance in contrast to the speaker whose attention is focused on the meaning mainly. Thus the level of the development of skills in writing can be somewhat lower than those of speaking. Competence in writing embraces skills, knowledge and communicative abilities. Skillspresuppose technical skills (graphic and spelling), grammar skills and vocabulary skills (among them those skills that ensure coherence and cohesiveness of the text are very important) as well as communicative skills of writing. Communicative skills of writing include the following skills: · to make up sentences and texts according to the requirements of communication in a written form; · to ensure coherence, cohesiveness, completeness and addressed character of the texts; · to provide for the appropriate style, register and genre; · to structure texts according to the type and genre; · to provide for socio-cultural requirements to the text genre and type; · to render the content of the original text in a short form etc. Intellectual skills embrace skills to take into consideration the target audience (the addressee, the situation, possible reaction etc); to plan and programme utterances; to construct them logically; to give arguments; to generalize etc. Compensational skills: to paraphrase, to simplify structures, to support writing with the information inferred from the text for reading or listening etc. Knowledgeincludes linguistic knowledge (of spelling rules; syntactic rules; vocabulary, grammar and cohesive devices as well as stylistic means characteristic for the text type and genre etc), cross-cultural and sociolinguocultural knowledge (e.g. some patterns, standards for a certain genre), knowledge of compensational strategiesetc. Communicative abilities necessary for effective writing embrace inner motivation to become a member of communication through producing texts of different genres; ability to take the addressee into consideration when expressing your own ideas and intentions and to predict their reaction (to ensure that the addressee perceive the text in the way the writer expects it); to choose form and content of the written utterance consciously and effectively by constant changes and self-correction; to induce the addressee to certain verbal and non-verbal acts etc. Teaching techniques of writing Graphic and spelling skills are based on certain knowledge and language awareness. The process of mastering these skills is complicated by three groups of factors: learners’ individual characteristics, the target language features and the learning and teaching conditions (the teacher, teaching technologies, and teaching materials). Learners’ individual characteristics: their visual memory, attention, ability to write well in their mother tongue, ability to perform logical operations (compare, contrast, use analogy, conclude etc). The target language features: similarities and differences in graphic systems of the native and target languages (a, o, e, p - small and capital letters are the same; M, H, B – only capital letters are similar while small letters – m, h, b – are different; both capital and small letters are completely different – s, f, q, r, j, v, z). It is especially difficult for young learners to differentiate b and d, to write Latin k instead of Ukrainian, to get aware of the elements that should be above or below the line (f, h, j, q) etc. Spelling system of English is based on several principles: phonetic, when graphic form corresponds to sound form (dog, pen); morphologic, when each morpheme (prefix, root, suffix) preserves the same sound form in different positions (nation-nationality); historical, when spelling is connected with traditions and historical development of a word (busy, two, school). The last principle predominates in English spelling. Letter and sound correspondences also cause difficulties: one letter – several sounds (s – 4 sounds), one sound – by several letters (ir, er, ur), several digraphs - one sound (ch, th, sh), silent letters (e at the end, wh, wr, ght) etc. Learning and teaching conditions: lack of teaching materials of high quality, badly planned or conducted lesson parts, lack of teachers’ awareness of the learners’ difficulties; insufficient account of age characteristics leading to inappropriate methods and teaching technologies. Graphic skills should be developed in primary school (first year). Orthographic skills - during all forms (primary, basic, senior). Activities to develop graphic skills are receptive-reproductive drills in copying the letters, letter combinations, words. It is advisable to begin with easiest letters and those which are used in the vocabulary units they study. · Grouping similarly shaped letters (e.g. a, c, d etc) · Letter recognition (find the same letter in several words, underline the letter, copy out words with the letter etc) Games are often used: · Help small and capital letters find each other and write down the pairs. · Small letters are lost. Find their parents (capital letters) and write them down. · Write letters according to the given numbers (numbers in the alphabet) Activities to develop spelling skills are also non-communicative drills (copying, copying and underlining some letters, copying and sorting out, copying homographs, copying only the selected words (with some letter combination, prefix, suffix), gap-filling, unjumbling words, finding words in letter squares, group words according to spelling rules, matching halves of the words, etc.). These activities also include reproducing words according to their definitions, native equivalents, pictures (crosswords, game “Wonderland”) and writing down words (dictations: visual, auditory, explanatory, self-dictations, running dictations etc).
|