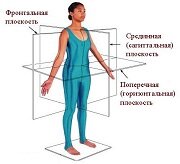
ПОЗНАВАТЕЛЬНОЕ Сила воли ведет к действию, а позитивные действия формируют позитивное отношение Как определить диапазон голоса - ваш вокал Игровые автоматы с быстрым выводом Как самому избавиться от обидчивости Противоречивые взгляды на качества, присущие мужчинам Вкуснейший "Салат из свеклы с чесноком" Натюрморт и его изобразительные возможности Применение, как принимать мумие? Мумие для волос, лица, при переломах, при кровотечении и т.д. Как научиться брать на себя ответственность Зачем нужны границы в отношениях с детьми? Световозвращающие элементы на детской одежде Как победить свой возраст? Восемь уникальных способов, которые помогут достичь долголетия Классификация ожирения по ИМТ (ВОЗ) Глава 3. Завет мужчины с женщиной Оси и плоскости тела человека - Тело человека состоит из определенных топографических частей и участков, в которых расположены органы, мышцы, сосуды, нервы и т.д.
| The System of Secondary Education in Britain
In England about 93 per cent of children attend state schools, which provide free education. They are financed by public funds, which means that the money comes from the national and local taxes. The other 7 per cent attend independent schools - private or public schools. Education in Great Britain is compulsory and free for all children between the ages of 5 and 16. There are many children who attend a nursery school from the age of 3, but it is not compulsory. In nursery schools they learn some elementary things such as numbers, colours, and letters. Apart from that, babies play, have lunch and sleep there. Whatever they do, there is always someone keeping an eye on them. Compulsory education begins at the age of 5 when children go to primary school. Primary education lasts for 6 years. It is divided into two periods: infant schools (pupils from 5 to 7 years old) and junior schools (pupils from 7 to 11 years old). In infant schools children don't have real classes, there is no written time table. Much time is spent in modelling from clay, drawing, reading, climbing frame. They mostly play and learn through playing. It is the time when children just get acquainted with the classroom, the blackboard, desks and the teacher. But when pupils are 7, real studying begins. They don't already play so much as they did it in infant school. Now they have real classes, when they sit at desks, read, write and answer the teacher's questions. In Year 3 the "real work" starts. The children have lessor in arithmetic, reading and composition. History, Geography, Nature Study Art and Music, PE, Swimming are also in the timetable. All schools follow the same National Curriculum. The children attend the primary school for 6 years . Сompulsory secondary education begins when children are 11 or 12 and lasts for 5 years. Secondary school is traditionally divided into 5 forms: a form to each year. Children study English, Mathematics, Science, History, Art, Geography, Music, a Foreign language and have lessons of Physical training. Religious education is also provided. English, Mathematics and Science are called "core" subjects. At the age of 7,11 and 14 pupils take examinations in the core subjects. There are 3 types of state secondary schools in Great Britain. They are: 1) comprehensive schools, which take pupils of all abilities without exams. In such schools pupils are often put into certain sets or groups, which are formed according to their abilities for technical or humanitarian subjects. Almost all senior pupils (around 90 per cent) go there; 2) grammar schools, which give secondary education of a very high standard. Entrance is based on the test of ability, usually at 11. Grammar schools are single sexed schools; 3) modern schools, which don't prepare pupils for universities. Education in such schools gives good prospects for practical jobs. After five years of secondary education, at the age of 16, pupils take the General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) examination. When they are in the third or in the fourth form, they begin to choose their exam subjects and prepare for them. After finishing the fifth form pupils can make their choice: they may either leave school and go to a Further Education College or continue their education in the sixth form. Those who stay at school after GCSE, study for 2 more years for "A' (Advanced) Level Exams in two or three subjects which is necessary to get a place at one of British universities. There are also about 500 private schools in Great Britain. Most of these schools are boarding ones, where children live as well as study. Education in such schools is very expensive, that's why only 5 per cent of schoolchildren attend them. Private schools are also called preparatory (for children up to 13 years old) and public schools (for pupils from 13 to 18 years old). Any pupil can enter the best university of the country after leaving this school. The most famous British public schools are Eton, Harrow and Winchester. After leaving a secondary school young people can apply to a university, a polytechnic or a college of further education.
|